The worst got worser — and drove more.
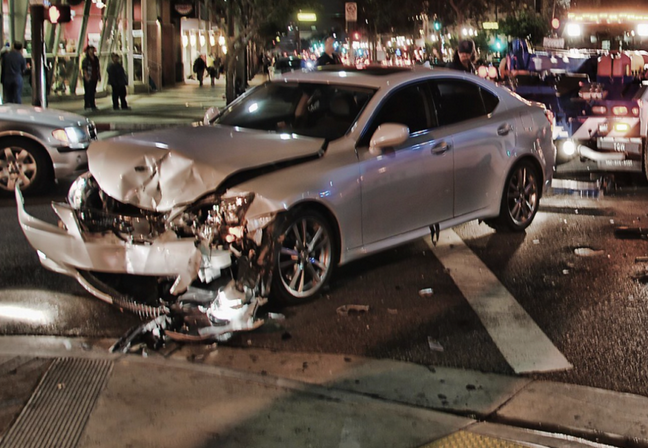
A new survey by the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety shows that America's worst driver reacted to the pandemic by driving much more dangerously — and by driving more, which partly explains why traffic fatalities and the rate of fatalities per mile increased during the pandemic.
“Our research finds that higher-risk motorists accounted for a greater share of drivers during the pandemic than before it,” said Dr. David Yang, the foundation's executive director. “Safety-minded individuals drove less, while many who increased their driving tended to engage in riskier behaviors behind the wheel.”
There's actually two things going on: first, the people who reduced their driving during the pandemic tended to be into or past middle-age and also more likely to be female — which are two statistically safer-than-average driving populations. The drivers who drove more during the pandemic "were predominantly younger and male — a statistically higher-risk group," the survey said.
But the second related danger factor is that those drivers who were already prone to violence acted even more recklessly during the pandemic, according to the survey.
For instance, the cohort of people who said they drove more were also:
- Twice as likely to say they texted while driving.
- More than 44 percent more likely to speed on highways and residential streets.
- Eighty percent more likely to run red lights.
- More than twice as likely to make aggressive lane changes.
- About 133 percent more likely to drive without a seatbelt.
- And nearly three times as likely to drive drunk or high.
Of note, only 4 percent of the survey group reported an increase in driving during the pandemic, but if that percentage were told hold across the entire nation, it would clearly indicate that "at least some of the increase in crash rates observed during the Covid-19 pandemic may be attributable to an increase in driving among a small subset of drivers with both higher baseline risk and greater propensity to engage in risky driving behaviors."
The survey does not explain why already dangerous drivers got more reckless, but it does cite prior reports that enforcement dropped dramatically during the early days of the pandemic. And it also mentions a 2021 study that concluded that the reduction in road traffic also reduced drivers’ perceptions "of the risk and difficulty of the driving task ... relative to typical pre-pandemic driving situations."
The AAA Foundation study stopped short of making any recommendations for getting the most dangerous drivers off the road, whether through enforcement, better transit or economic incentives, nor does it advocate for road redesign that can make it more difficult for even the most negligent drivers to do damage.