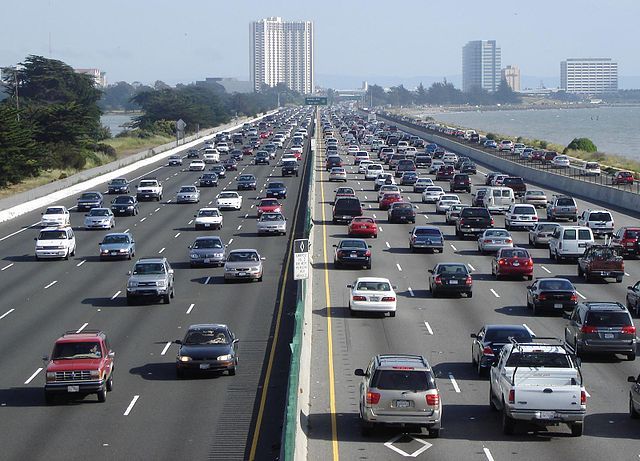
Urban planners should abandon their obsession with fighting congestion in favor of building more housing in traffic-choked cities because people who live in congested urban centers actually have better access to good jobs and economic opportunity, a new study reveals.
It's no great surprise that the best jobs in the study region — the San Francisco Bay Area — are in congested areas, but, according to the study by a team of UCLA researchers, commuters who lived near uncongested highways on the fringes of the region couldn't get to the best jobs faster than people living within the high-traffic areas.
"The most densely developed places typically offer the highest levels of access, despite typically higher levels of congestion," the researchers wrote in the study, which was published in May in the journal Transportation Research Part A.
The study analyzed the number of jobs available to the 8.2 million people living in the nine counties making up the San Francisco Bay Area. The authors calculated the number of jobs available to commuters living in 1,454 "zones" across the region, cross-referencing data on travel time, distance, speed and job locations.
Those living in the most central zones had greater proximity to jobs, including higher-paying IT jobs, despite the congestion. The higher rate of speed enjoyed by exurban residents couldn't make up the difference, the study found. In fact, proximity was almost three times greater a predictor of job access than speed. For IT jobs — which the study assumed people were willing to travel farther for because of the greater pay — the effect was much more pronounced: 18 times greater for proximity than speed.
Even if congestion could be dramatically improved across the Bay Area, the authors found, the effects on job access would be relatively minor. As frustrating as congestion is to drivers, only 5 to 12 percent of the region's residents would see an "appreciable" increase in job access if congestion was essentially eliminated, the job access models the team created showed. That, practically speaking, would be impossible or cost prohibitive to accomplish anyway.
The findings shouldn't be surprising to anyone with even a passing knowledge of real estate prices in the Bay Area. But the proximity effect — the more important factor from a worker's perspective — has been almost entirely ignored by the highway planning profession, which has spent billions trying to relieve congestion on urban highways, and largely ignoring the role that land use plays in people's travel behavior.
Workers in metro regions would clearly be better served by more affordable housing options near jobs, the authors said, recommending infill housing in the urban core.
Hat Tip: Tim Kovach