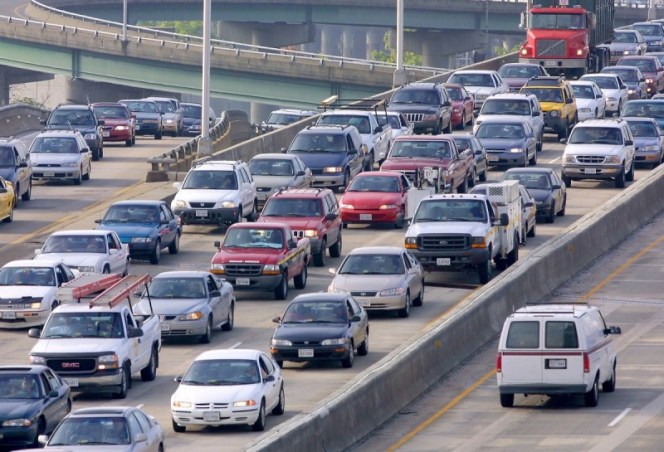
Whenever city rankings of traffic congestion come out, there's always a round of coverage about curing gridlock with wider roads -- a strategy that never solves the problem. Instead we should be focusing our attention on eliminating all the incentives that favor driving.
Among the more galling subsidies, writes Susan Balding at Greater Greater Washington, are commuter parking benefits. Many employers provide free parking as a perk, and the federal tax code allows car commuters to write off up to $255 a month in parking expenses.
Thanks to a change in the law in 2015, transit riders can write off the same amount, but the impact is overwhelmed by the traffic-inducing effect of the parking benefit. Baldwin says if we're going to make a dent in congestion in major cities, parking subsidies have got to go:
DC, San Francisco, and New York City have all passed laws requiring employers of a certain size to let employees spend their own money tax-free to buy transit fares. According to DDOT, 78% of employers in DC started offering pre-tax transit benefits because of the law.
Nonetheless, employers who offer to pay for part or all of their workers' parking can be a lot more attractive than those who just allow employees to buy pre-tax transit fares. In DC, 34 percent of employers offer free parking, and an additional 18 percent offer an employer-paid parking subsidy.
If you work somewhere where parking is free and abundant, a parking benefit doesn't really affect you. But if you’re commuting in a place where parking costs money -- for example, downtown DC -- this benefit is very real, as it makes driving cheaper, but transit still costs the same.
Parking benefits, you likely won’t be surprised to hear, also drive up congestion. And beyond that, they leave governments with even less money to repair roads and keep up public transit systems: As of 2014, the parking benefit translated into about $7 billion a year in lost tax revenue (because the money used toward the benefit is not taxed). To put that in perspective, the Federal Transit Administration’s total appropriations in 2016 came to just over $11 billion.
More recommended reading today: Capital Metroblog reports that Austin is planning to move forward with a bus system redesign much like Houston's. And Green Caltrain considers whether the Trump administration's interference with Caltrain electrification signals hostility to transit projects in the rest of the nation too.