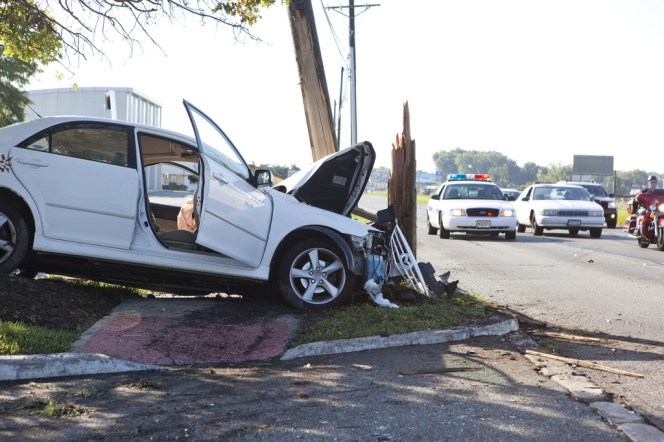
What if you could reliably pinpoint the street segments all over the country where speeding traffic poses a constant threat to life and limb? That could be a very powerful tool to identify and redesign dangerous streets.
At a time when traffic fatalities are rising rapidly and the National Transportation Safety Board acknowledges that excessive vehicle speeds contribute to America's sky-high traffic death rate, the time is ripe for that kind of analysis.
Two transportation researchers say a national map of dangerous traffic speeds could be possible. Eric Sundquist and Michael Brenneis at the State Smart Transportation Initiative report that U.S. DOT has purchased a vast set of traffic speed data collected by the firm INRIX, which it will share with state DOTs.
The feds aren't thinking about analyzing speed as a safety problem, however. "The US DOT is buying the data from INRIX so that DOTs can comply with performance measure requirements around delay and reliability," Sundquist and Brenneis write. In other words, U.S. DOT is thinking about congestion and traffic delay.
But with the data now in the hands of state DOTs, Sundquist and Brenneis say there's no reason it can't be used to save lives:
One application we haven’t seen -- and we’d like to hear from anyone doing it or interested in doing so -- is for speed management.
The notion is simple: The data provide average speeds by time and place, which can pinpoint congestion and reliability issues. They also indicate areas with excessive traffic speed. And while federal performance measures focus on the former, it’s possible to imagine speed management measures as well.
And in fact some exist. This is a measure established by the city of Los Angeles: “Ensure that 80% of street segments do not exceed targeted operating speeds by 2035.”
The data isn't as fine-grained as detailed speed studies, which capture the distribution of driver speeds, not just the average. But Sundquist and Brenneis believe that average speed can still be a useful metric to identify dangerous conditions. They're asking researchers who want to refine these ideas to contact them.
More recommended reading today: Plan Philly reports on SEPTA's plans to improve service and increase ridership by redesigning its network of 126 bus routes. And Better Burque shares photos of "Suddenly Ending Bike Lanes" around Albuquerque.